PPTC and ESD Protection in TWS Headset Protection Systems
Overview
The True Wireless Stereo (TWS) headset market has grown exponentially with the increasing popularity of wireless audio devices. TWS headsets offer convenience, portability, and high-quality sound, making them a popular choice for consumers. However, with their advanced features, such as Bluetooth connectivity, touch controls, noise cancellation, and high-quality audio, TWS headsets also come with a range of electronic components that need to be carefully protected against over current and electrostatic discharge (ESD) events.
Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC) resistors and ESD protection devices are key components used to safeguard TWS headsets from potentially damaging electrical events. PPTCs protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions, while ESD protection components shield sensitive electronic parts from high-voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge. Together, these components ensure the reliability, durability, and long lifespan of TWS headsets.

This case study discusses the application of PPTC and ESD protection in TWS headsets from the perspective of a resistor manufacturer, highlighting how these components enhance the safety and performance of TWS devices.
The Role of PPTC and ESD Protection in TWS Headsets
TWS headsets typically include a number of electronic components that need protection against electrical risks. These risks include overcurrent, overvoltage, and static electricity that can damage the sensitive circuits, battery, and charging interfaces. PPTC and ESD protection components play a crucial role in safeguarding these devices.
1. PPTC Protection: Overcurrent Protection in TWS Headsets
PPTC resistors are used in TWS headsets to protect the device from overcurrent situations, such as excessive current flow due to a short circuit or other electrical fault. PPTC resistors are a form of self-resetting fuse that increase their resistance when a fault condition (such as an overcurrent) occurs, thereby limiting current flow and protecting the circuit. When the fault condition is cleared and the device cools down, the PPTC automatically resets itself, allowing normal operation to resume.
Applications of PPTC in TWS Headset Protection:
1. Battery Protection:
The battery in a TWS headset is a critical component that can be easily damaged by overcurrent, which could occur during charging, discharging, or due to a short circuit. A PPTC resistor is placed in the power path to protect the battery from excessive current that could overheat or cause permanent damage to the battery cells.
2. Charging Circuit Protection:
The charging circuitry in TWS headsets, which includes components like charging ICs and the charging port, is susceptible to overcurrent during the charging process. A PPTC resistor can be used to limit the current in case of a charging malfunction, preventing damage to these critical components.
3. USB Port and Connector Protection:
TWS headsets often use a USB-C or Micro-USB connector for charging. These connectors can become damaged due to improper insertion or a short circuit. PPTC devices can be placed in the power path of these connectors to safeguard them against overcurrent and misuse, ensuring the device does not suffer permanent damage.
Benefits of PPTC in TWS Headsets:
Self-resetting: Unlike traditional fuses, PPTC resistors automatically reset after the overcurrent condition is cleared, making them more reliable for long-term use.
Small Form Factor: PPTC devices are compact and can be easily integrated into the small form factor of TWS headsets.
Reliable Protection: PPTC resistors provide consistent overcurrent protection, enhancing the safety and longevity of TWS headsets.
2. ESD Protection: Protecting TWS Headsets from Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) is a common issue in consumer electronics, especially in devices like TWS headsets, where there are many sensitive electronic components packed into small, confined spaces. ESD events can occur when a person interacts with the device, such as touching the charging port or connector, or when the device comes into contact with materials that generate static electricity. These high-voltage spikes can damage semiconductors, integrated circuits (ICs), and other delicate components in the headset.
ESD protection devices are used to shunt or redirect the energy from an electrostatic discharge away from the sensitive circuits and into a safe path, preventing damage to the internal components. There are various types of ESD protection components, such as TVS diodes, varistors, and ESD resistors, each designed to absorb high-voltage surges and dissipate the energy harmlessly.
Applications of ESD Protection in TWS Headsets:
1. Connector and Charging Port Protection:
The charging port of a TWS headset is an area vulnerable to electrostatic discharge, especially when the device is plugged into a charging cable. ESD protection devices are commonly placed across the charging pins or the power input circuitry to absorb any static voltage that might arise during handling or connection to a charger.
2. Touch and Control Button Protection:
TWS headsets often have touch-sensitive controls for adjusting volume, play/pause, and power. These touch pads are susceptible to ESD, which could cause malfunctioning or damage to the capacitive sensors. ESD protection components are used to shield these interfaces and prevent static from affecting the functionality.
3. Bluetooth and Wireless Connectivity Circuits:
The Bluetooth chipset in a TWS headset, which handles the wireless communication, is also vulnerable to ESD events. By placing TVS diodes or ESD resistors in the signal paths of the Bluetooth module, manufacturers can protect the module from electrostatic surges that may interfere with performance or cause permanent damage.
Benefits of ESD Protection in TWS Headsets:
Effective Protection: ESD protection devices can absorb high-voltage surges, protecting the sensitive electronics from irreversible damage and preserving the functionality of the device.
Compact and Lightweight: ESD protection components are available in small form factors, allowing integration into the compact design of TWS headsets without adding significant size or weight.
Long-Term Reliability: By preventing damage from ESD, these components help maintain the long-term reliability and durability of TWS headsets, ensuring they continue to function properly even after extended use.
How PPTC and ESD Protection Work Together in TWS Headsets
PPTC resistors and ESD protection devices work in tandem to provide comprehensive protection for TWS headsets. Together, they address two of the most common causes of failure in electronic devices: overcurrent and electrostatic discharge.
1. PPTC for Overcurrent:
During charging or usage, if the TWS headset experiences excessive current (e.g., due to a short circuit, defective charger, or battery malfunction), the PPTC resistor will increase its resistance, limiting the current flow and preventing the device’s internal components from overheating or burning out.
2. ESD Protection for Electrostatic Discharge:
If the user introduces static electricity into the system (e.g., by touching the charging port or connectors), the ESD protection device will absorb and safely redirect the voltage spike, ensuring that the sensitive components, such as the Bluetooth module and touch sensors, are not damaged by the discharge.
In combination, these two types of protection ensure that TWS headsets can withstand both overcurrent conditions and electrostatic discharge events, significantly enhancing their durability, safety, and performance over time.
Key Benefits of PPTC and ESD Protection in TWS Headsets
1. Comprehensive Protection:
PPTC resistors provide overcurrent protection, while ESD protection devices safeguard the headset from electrostatic discharges, offering a dual-layer defense against electrical threats.
2. Improved Reliability and Longevity:
Both PPTC and ESD protection devices extend the life of TWS headsets by preventing damage caused by overcurrent or ESD, reducing the likelihood of product failures and malfunctions.
3. Compact Integration:
The small size of PPTC and ESD protection devices allows them to be integrated into the compact designs of TWS headsets without taking up significant space or adding weight.
4. Cost-Effective Safety:
Using PPTC and ESD protection components is a cost-effective way to ensure the safety of TWS headsets, preventing expensive warranty claims or repairs due to electrical damage.
5. Compliance with Industry Standards:
ESD protection and overcurrent protection are important for ensuring compliance with global standards for consumer electronics, such as IEC 61000-4-2 for ESD immunity, and UL safety standards.
Conclusion
The growing demand for True Wireless Stereo (TWS) headsets has led to the development of advanced protection systems to safeguard these devices from common electrical hazards. As a resistor manufacturer, we see the value in providing PPTC resistors for overcurrent protection and ESD protection devices to shield sensitive electronics from electrostatic discharge. These components play a vital role in ensuring that TWS headsets remain safe, reliable, and durable in the hands of consumers.
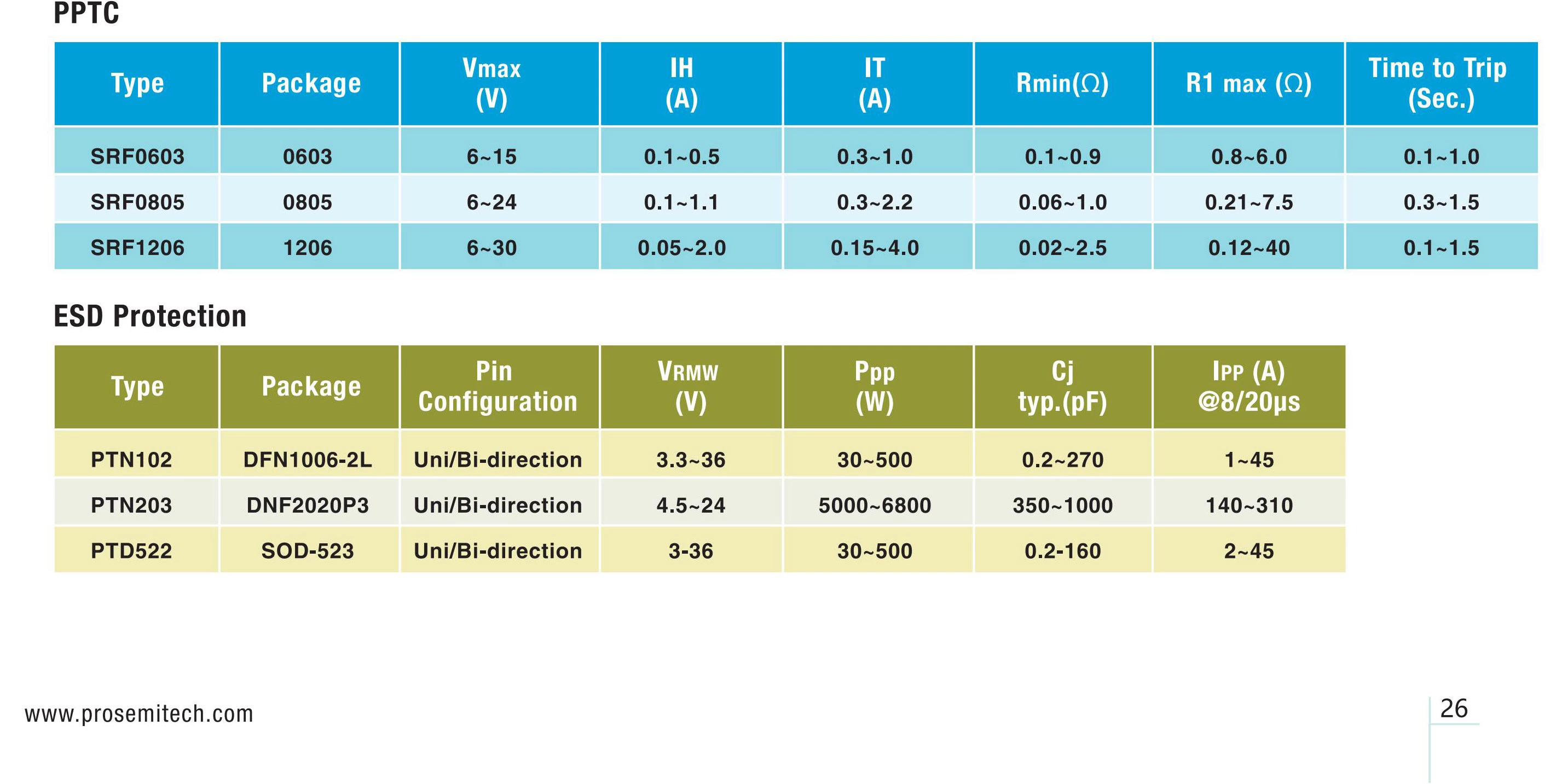
By integrating PPTC resistors
and ESD protection devices into the TWS headset design, manufacturers can offer products that are better equipped to handle the challenges of everyday use, such as charging mishaps, static discharge, and overcurrent events. In doing so, we help create a more resilient, long-lasting, and customer-friendly product, ultimately driving the success of TWS headsets in the competitive consumer electronics market.